...
Collections of picos are used to create models of interacting entities in the Internet of Things. Picos communicate by sending events to or making requests of each other in anActoran actor-like manner. These communications are point-to-point and every pico can have a unique address, shared by no one else, to any other pico to which it communicates. Collections of picos were used in architecting the Fuse connected-car system with significant advantage.
...
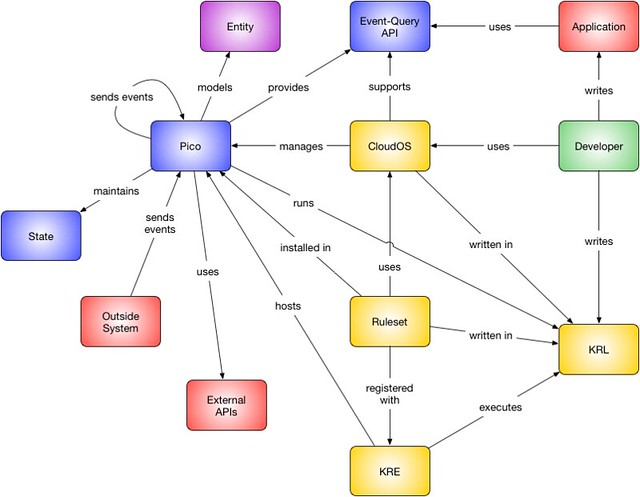
The various pieces of the pico ecosystem and their relationship is shown in the following diagram (click for enlarged diagram).
For people who've read this blog, many Many of the titles in these boxes will may be familiar, but I suspect that the exact nature of how they relate to each other has been a mystery in many cases. Here are some brief descriptions of the primary components and some explanation of the relationships.
...
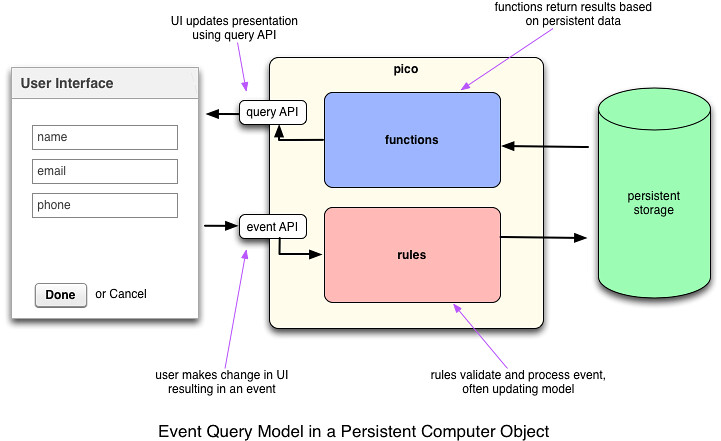
The event-query API is a name I gave the style of interaction that picos support. Picos don't implement RESTful APIs. They aren't meant to. As I explain in Pico APIs: Events and Queries, picos are primarily event-driven but also support a query API for getting values from the pico. Each pico has an internal event-bus. So while picos interact with each other and the world in a point-to-point Actor modelactor model, internally, they distribute events with a publish and subscribe mechanism. More
...
The following diagram shows the rules and functions in a pico presenting an event-query API to an application.
CloudOS Wrangler provides functionality to installing rulesets in a pico and they can change overtime just as the programs installed on a computer change over time. As the installed rulesets change, so does the pico's API.
KRL
KRL is the language in which rulesets are programmed. Picos run KRL using the event evaulation evaluation cycle. Rules in KRL are "event-condition-action" rules because they tie together an event expression, a condition, and an action. Event expressions are how rules subscribe to specific events on the pico's event bus. KRL supports complex, declarative event expressions. KRL also supports persistent variables, which is how developers access the pico's state. KRL developers do not need a database to store attributes for the pico because of persistent variables.
...
The pico engine is a host or container engine for picos. A given instance of the pico engine can host any number of picos. The pico engine makes picos work. Pico Engine is an open source project, hosted on GithubGitHub.
KRL rulesets are usually hosted online. Developers register the URL with a pico engine to create a ruleset ID or RID. A given ruleset can be installed in any number of picos. When the pico runs, the engine gets the ruleset source, parses it, optimizes it, and executes it.
...
Picos present a powerful model for how a decentralized, heterarchical, interoperable Internet of Things can be built. Picos are built run on open-source software and support a unbiased hosting model for deploymentengine that can be deployed on any hardware that supports Node JS. They have been used to build and deploy several production systems, including the Fuse connected-car system. They provide the means for giving people direct, unintermediated control of their personal data and the devices that are generating it.
...