This page will guide you through the steps necessary to obtain and operate your own Kinetic Rules Engine (KRE).
Learning Objectives
After completing this quickstart lesson, you will:
- understand important concepts about programming in KRL including ruleset structure*
- know how to install and operate the node pico-engine
- know how to use your Engine Rulesets page to register a ruleset
- know how to add a ruleset to a Pico
Concepts
*This section is copied verbatim from Quickstart
Getting started with KRL can be a big leap because there are so many things that are different about programming in KRL:
- KRL is a rule-based language.
- KRL primarily follows an event-based programming model.
- KRL programs execute with a cloud-based model; there is no way to execute them from the command line.
- KRL programs are loaded from the cloud using HTTP.
- KRL programs execute in a system where identity is pervasive; all events are raised on behalf of a specific entity.
- KRL programs have built-in, entity-specific persistent storage; there is no need for external databases.
The result of these properties is a programming model that more closely resembles programming cloud-based persistent objects than anything else. We call these persistent computational objects "picos".
KRL is executed by your instance of the node pico-engine, an open-source, cloud-based rule processing system. All of the properties listed above are present in any KRE system.
Install and run the node pico-engine
Prerequisite: you will need to install node (also known as Node.js) on your machine. It includes npm, the node package manager.
- clone from the repository at https://github.com/Picolab/node-pico-engine
- change into the folder named "node-pico-engine"
- run the command `npm install`
- choose a port number for the web server which the pico-engine implements (the default is 8080)
- start the pico-engine web server
The web server will display the URL of its document root, ex. http://localhost:8080
Create a Pico
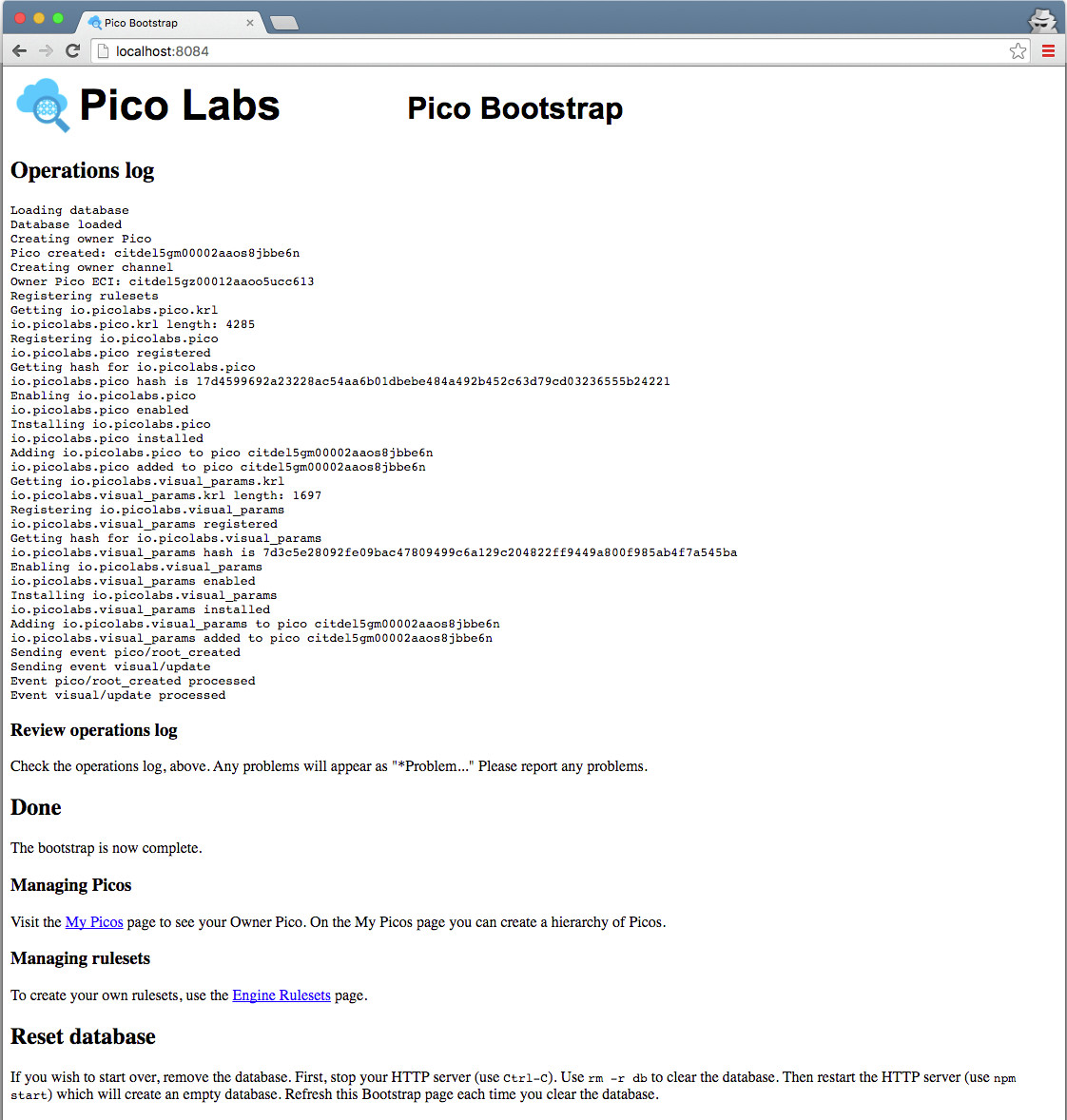
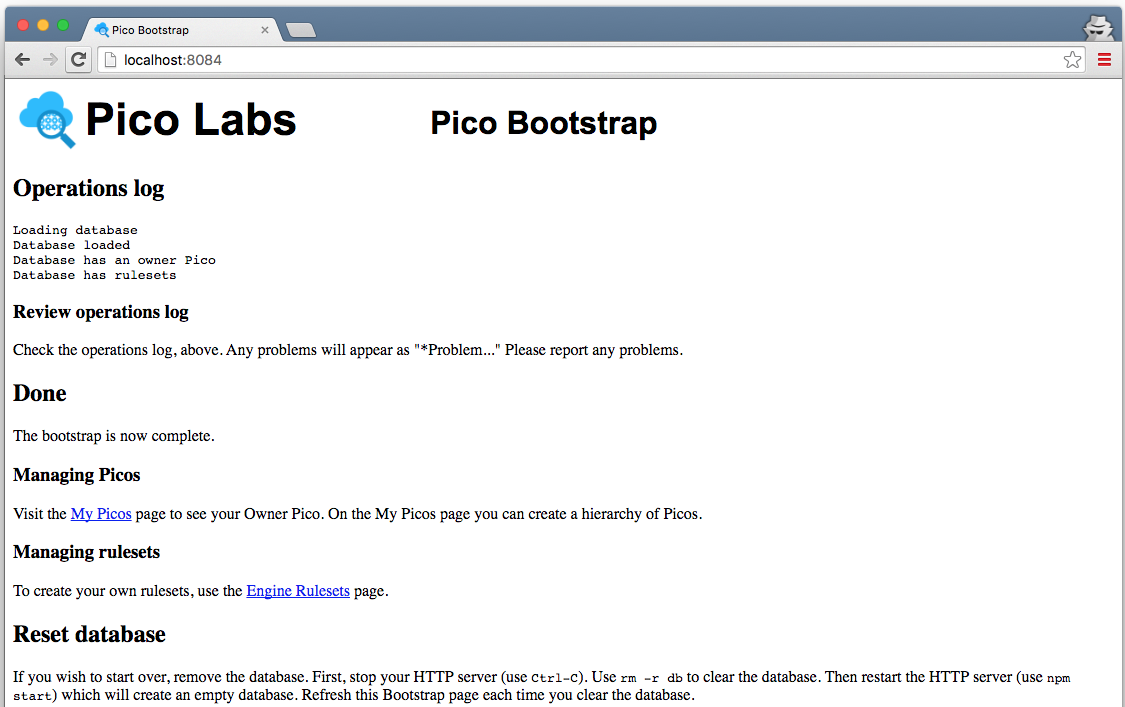
Visit the default web page of your web server. As this page loads, it will perform a bootstrap sequence, which creates a Pico, known as "Owner Pico" and then registers and installs two rulesets.
Subsequent visits to the same page will short-circuit the bootstrap (because it's already been done).
Writing KRL
Here is a sample KRL ruleset:
ruleset hello_world {
meta {
name "Hello World"
description <<
A first ruleset for the Quickstart
>>
author "Phil Windley"
logging on
shares hello
}
global {
hello = function(obj) {
msg = "Hello " + obj;
msg
}
}
rule hello_world {
select when echo hello
send_directive("say") with
something = "Hello World"
}
}
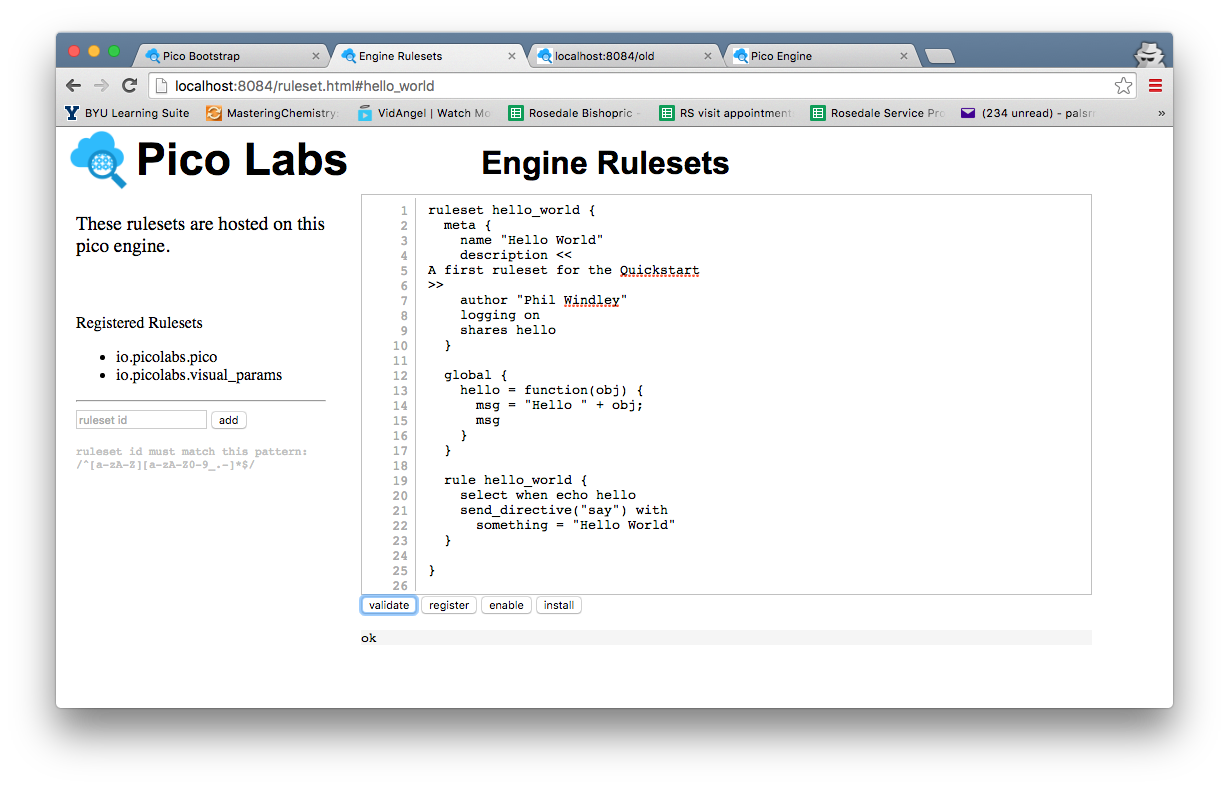
Enter the ruleset name "hello_world" into the box in the Engine Rulesets page, and click the "Add ruleset" button. Then complete the ruleset, and click the "Verify" button. When your KRL compiles correctly, you will see a result of "ok" beneath the buttons.
Hint: you should also save your ruleset somewhere in your file system, named, say "hello_world.krl" as the editor in the Engine Rulesets page is very primitive and does not have a "save to disk" option.
Click on the "register" button. Notice the circle beside the ruleset name. This indicates that the source code has been registered with the pico-engine, but is not yet enabled. Click on the "enable" button.
Finally, click on the "install" button. This causes the engine to compile the KRL and cache the compiled version in the "rulesets" folder. Once this has been done, the ruleset can be added to Picos.